RavenDb 4 Part 2 - Client Configuration
Part 1 of this article can be found here
Architecture Diagram
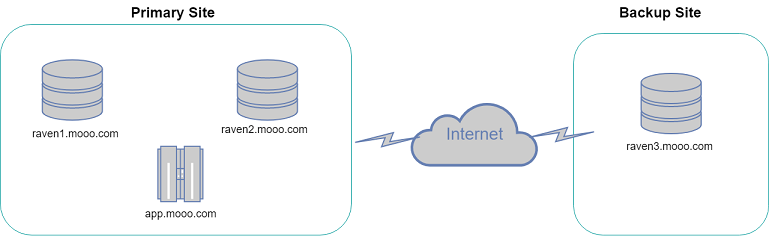
Now we have our RavenDb servers set up lets create a web app from scratch that will communicate with the RavenDb cluster.
dotnet new webapp -o ravendemo
dotnet add package RavenDB.Client --version 4.1.5
dotnet add package Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting.WindowsServices
We need our web app to be able to run as a service so in Program.cs replace CreateWebHostBuilder(args).Build().Run with:
var host = CreateWebHostBuilder(args).Build();
var isService = args.Contains("--service");
if (isService)
{
var baseDirectory = new FileInfo(Assembly.GetEntryAssembly().Location).Directory.FullName;
Directory.SetCurrentDirectory(baseDirectory);
}
if (isService)
{
ServiceBase.Run(new WebHostService(host));
}
else
{
host.Run();
}
Lets now add some code to configure the RavenDb DocumentStore singleton. Be sure to copy client.pfx to the output directory. For brevity the definition of the `Order class has been omitted.
var store = new DocumentStore { Urls = new[] { "https://raven1.mooo.com:8080" }, Database="TestDb"};
store.Conventions.IdentityPartsSeparator = "-";
X509Certificate2 certificate = new X509Certificate2(Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "client.pfx"));
store.Certificate = certificate;
store.Initialize();
using(var session = store.OpenSession())
{
session.Store(new Order { Name=Guid.NewGuid().ToString()});
session.SaveChanges();
}
When you run this you receive an error
The SSL connection could not be established, see inner exception. -> The remote certificate is invalid according to the validation procedure.'
The certificate is not trusted as it is signed by an untrusted CA. Fix this by importing client.pfx which also contains the CA certificate. Note that this time we will import the certificate into Local Computer by omitting the -user flag. You will thus need to run the following in an Admin Powershell prompt:
certutil -f -importpfx z:\client.pfx
Re-run the app in Visual Studio Code and it should work this time.
This approach has a drawback in that client.pfx must be used and the password exposed potentially in a config file. An alternative is to use the Windows Certificate Store to grant access to the private key. Remove the code loading the client.pfx from a file and replace with:
var x509 = new X509Store(StoreLocation.LocalMachine);
x509.Open(OpenFlags.ReadOnly);
var certificate = x509.Certificates.Find(X509FindType.FindBySubjectName, "*.mooo.com", true)[0];
If you re-run the app it will most likely work. This is due to the fact that by default the Administrators will have access to the private keys of the cert that was imported prior.
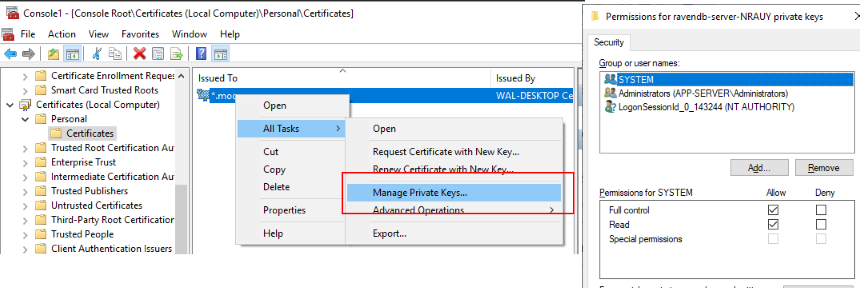
If you are running in a more locked down environment (or clear out the users in the dialog shown below) you get this error:
System.ComponentModel.Win32Exception: The credentials supplied to the package were not recognized
You will need to add yourself to the list of users who can access the private key (bring up the Dialog below via
mmc - > Add/Remove Snap-in -> Certificates -> Local Computer
Last revised: 27 May, 2019 05:39 AM History
No new comments are allowed on this post.
Comments
No comments yet. Be the first!